Traditional reservoir modeling practices using numerical simulators involve conversion of bottomhole pressures to surface wellhead or tubing pressure using VFP tables. Multiphase flow modeling of well stream is performed by means of interpolation from predefined liquid and gas rates. Simulation of transient flow in the well column is beyond the accuracy of common industry standard reservoir simulators. Liquid loading and accumulation, temperature profile, multiphase flow, and frictional pressure drop are just few examples of phenomena which will be neglected or over-simplified in traditional reservoir modeling.
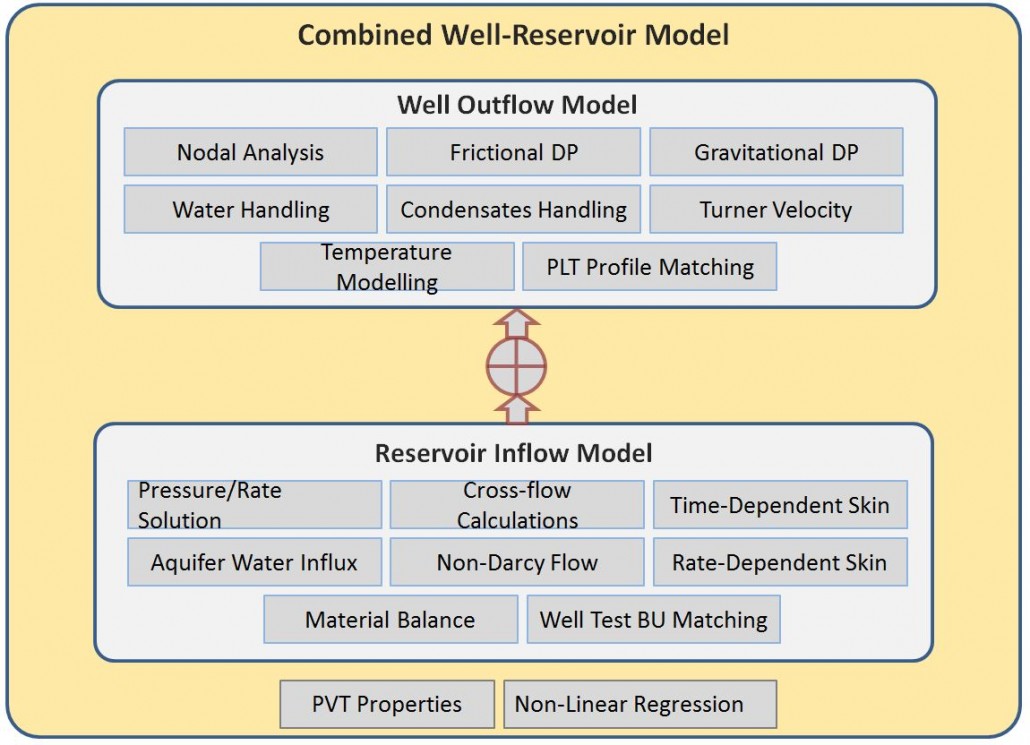
In Petroxin, we have developed a combined well and reservoir model to enhance our understanding of what really happens in the production system. Petroxin Combined Well-Reservoir Model, PeCWR, uses the advantage of an extensive library of analytical and empirical IPRs, completion types, aquifer models to model single or multilayered reservoir inflows. For well outflow performance, well known pressure drop correlations are used to model multiphase flow for vertical, horizontal or deviated sections.
Introduction of permanent downhole gauges (PDG) and fiber optic sensors in oil and gas wells enables operators to monitor well performance on a daily or even hourly basis. Pressure and temperature data are stored and can be used for precise well performance analysis, rate allocation and well problems diagnosis. In such cases, PeCWR can be used for modeling of multilayered reservoir to calculate individual layers contribution, cross-flows, zonal pressure, original and remaining fluid in-place and identify completion or well problems.
Key features of PeCWR include:
- Reservoir to surface simulation of oil, gas and gas condensate reservoirs
- Calculation of individual layers rates and pressures
- Prediction of recovery from individual layers and the whole drainage area
- Calculation of cross-flow between layers through the wellbore
- Identification of potential or problem layers
- Vertical flow profile in well column
- Oil and gas PVT properties calculation
- Vertical, horizontal and slant well nodal analysis
- Water vapor content and condensation calculation
- Top-bottom calculation for obtaining bottom-hole pressure
- Temperature modeling in the wellbore
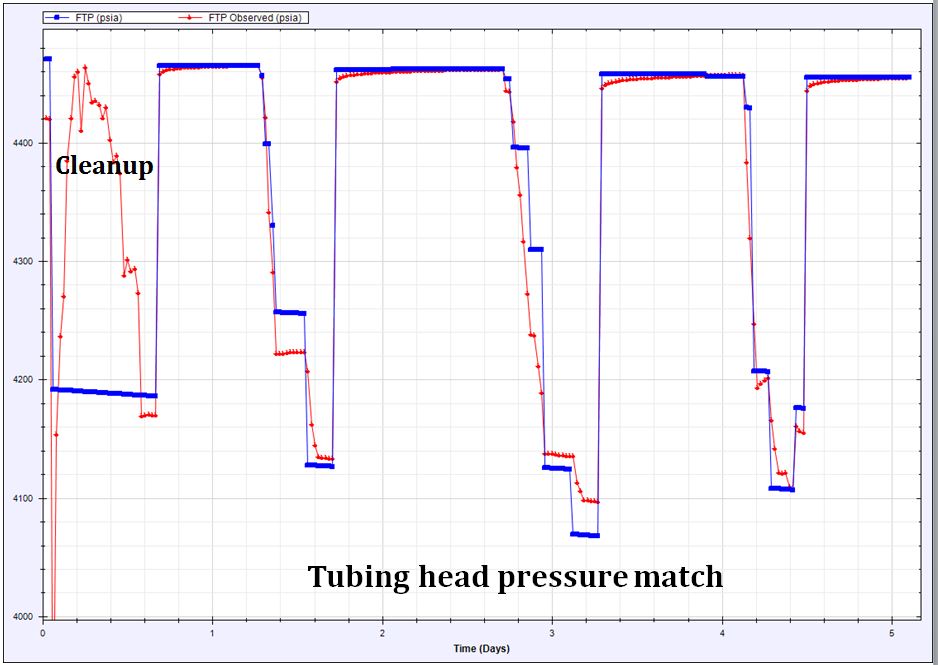
- History matching using PLT and production history
- Material balance check for calculation of remaining GIP
- Minimum velocity to lift liquids
- Non-Darcy gas flow option
- Inclusion of aquifers
- Handling water and condensate accumulation in the well